Cache Layer
The files corresponding to this layer can be found in the Cache directory. The code is to be written in the files RelCacheTable.cpp, AttrCacheTable.cpp and OpenRelTable.cpp. The declaration for the functions can be found in the respective header files RelCacheTable.h, AttrCacheTable.h and OpenRelTable.h.
Layout
Almost all operations on a relation require access to its corresponding Relation Catalog and Attribute Catalog entries. NITCbase stores these catalogs as relations in the disk. To prevent multiple reads and write backs of the catalog blocks, the Cache Layer caches the catalog blocks along with some extra metadata associated with the relation that allows faster and easier processing of operations such as search. The Cache Layer, thus, provides an interface for catalog access to the higher layers by hiding the storage and maintenance details of the catalogs. Cache Layer can cache a maximum of MAX_OPEN number of relations at any given time.
NITCbase requires that the relation be first loaded to cache memory before any operation is performed on it.
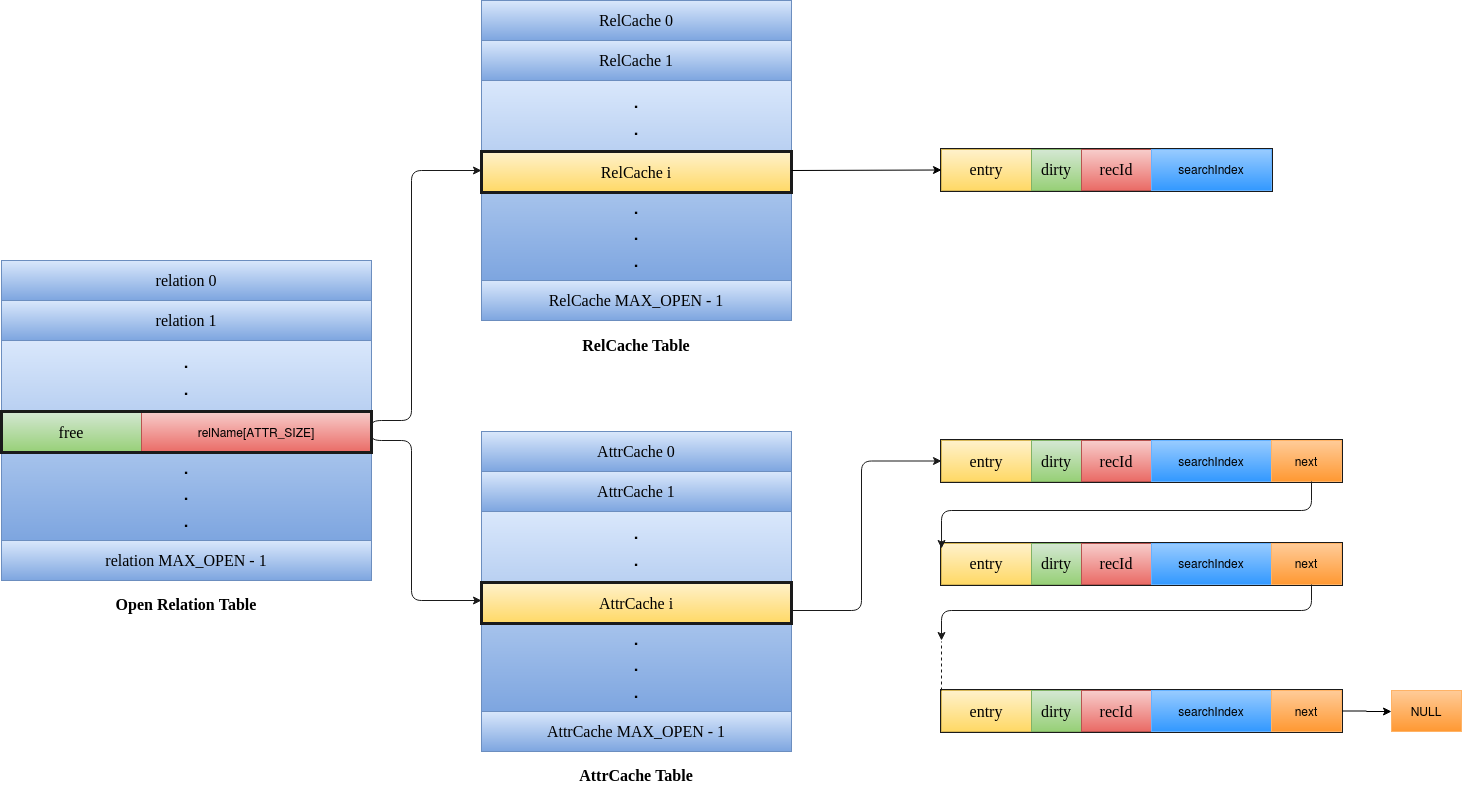
Three tables are used by NITCbase for caching Catalogs - the Relation Cache Table for Relation Catalog entries, the Attribute Cache Table for Attribute Catalog entries and the Open Relation Table to keep track of the entries stored in the other two catalogs.
NITCbase follows an Object-Oriented design for Cache Layer. The class diagram is as shown below.
Various structures used in the cache layer are outlined in the below diagrams.
relId
Any relation that is stored in the cache memory will have an entry in each of the three tables- Relation Cache Table, Attribute Cache Table, and Open Relation Table. An open relation is a relation that has been loaded to the cache memory while a closed relation is one that is not loaded to the cache memory (hence it is only present in the disk). NITCbase is designed in such a way that the entries in all the three tables will be stored at the same index.
This common index is called the relId of the relation and all further operations on the relation require this relId.
Relation Cache Table Structures
The Relation Catalog block in the disk stores metadata corresponding to all the relations in the database. In addition to this, the Relation Catalog entry of every open relation is loaded to the Relation Cache for easy access and for better performance. The Relation Cache is implemented in class RelCacheTable. Each entry in the Relation Cache stores all the attribute values of the relation's entry from the Relation Catalog along with some additional meta-data.
NITCbase caches Relation Catalog using two structures: RelCatEntry and RelCacheEntry.
RelCatEntry
The structure RelCatEntry stores all the attribute values in the relation's record entry from the Relation Catalog block in its data fields.
typedef struct RelCatEntry {
unsigned char relName[ATTR_SIZE];
int numAttrs;
int numRecs;
int firstBlk;
int lastBlk;
int numSlotsPerBlk;
} RelCatEntry;
RelCacheEntry
The structure RelCacheEntry stores the Relation Catalog entry of the relation along with some additonal information needed during runtime.
The RelCacheEntry data field details are as follows:
relCatEntry: Stores the relation's cached Relation Catalog entry.dirty: Indicates whether the Relation Catalog entry has been modified. The Relation Catalog entries with the dirty bit set are written back to disk when an open relation is closed.recId: Stores the record id{blockNum, slotNum}of the relation's entry in the Relation Catalog block on the disk. This is useful during the write back of the catalog entry to disk if it had been modified.searchIndex: Stores the record id{blockNum, slotNum}of the record block corresponding to the last (previous) search hit in the relation. Linear search algorithm of the Block Access Layer starts searching for the next hit from the previous hit location. The entries are initialized to{-1, -1}each time the relation is loaded to the cache memory. When every record of the relation has been searched, the linear search algorithm resets thesearchIndexvalue to{-1, -1}.
typedef struct RelCacheEntry {
RelCatEntry relCatEntry;
bool dirty;
RecId recId;
RecId searchIndex;
} RelCacheEntry;
Attribute Cache Table Structures
The Attribute Catalog blocks, analogous to the Relation Catalog block, stores the meta information of the attributes of all the relations in the database. In addition to this, the Attribute Catalog entries of every open relation is also loaded to the cache memory. This is implemented using Attribute Cache Table. Each entry in the Attribute Cache Table stores the entries corresponding to each attribute of the relation in the form a linked list along with some additional meta-data.
NITCbase caches Attribute Catalog using two structures: AttrCatEntry and AttrCacheEntry.
AttrCatEntry
The structure AttrCatEntry stores in its data fields all the attribute values in the record entry corresponding to one of the relation's attribute from an Attribute Catalog block.
typedef struct AttrCatEntry {
unsigned char relName[ATTR_SIZE];
unsigned char attrName[ATTR_SIZE];
int attrType;
bool primaryFlag;
int rootBlock;
int offset;
} AttrCatEntry;
AttrCacheEntry
The structure AttrCacheEntry stores the Attribute Catalog entry of an attribute of the relation along with some additonal information used during runtime. Since a relation can have variable number of attributes, a linked list of struct AttributeCacheEntry elements is maintained to cache all the Attribute Catalog entries together.
The AttrCacheEntry data field details are as follows:
attrCatEntry: Stores the cached Attribute Catalog entry corresponding to an attribute of the relation.dirty: Indicates whether the Attribute Catalog entry has been modified. The Attribute Catalog entries with the set dirty bit are written back to disk when an open relation is closed in the cache memory.recId: Stores the record id{blockNum, slotNum}of the record entry corresponding to the relation's attribute in the Attribute Catalog block on the disk. This is useful during the write back of the catalog entry to disk if it had been modified.searchIndex: Stores the index id{blockNum, indexNum}of the leaf index block corresponding to the last (previous) search hit for the attribute. This entry is used only if there is a B+ Tree created on the attribute. B+ Tree search algorithm of the B+ Tree Layer starts searching from the previous hit location for the next hit. The entries are initialized to{-1, -1}each time the relation is opened in the cache memory. When every Index Leaf Block entry of the B+ Tree has been searched, B+ Tree search resets the searchIndex value to{-1, -1}.next: Gives the pointer to the nextAttrCacheEntryelement in the linked list.
typedef struct AttrCacheEntry {
AttrCatEntry attrCatEntry;
bool dirty;
RecId recId;
IndexId searchIndex;
struct AttrCacheEntry *next;
} AttrCacheEntry;
Open Relation Table Structure
A relation must have an entry in the Open Relation Table for its Relation Catalog and Attribute Catalog entries to be cached in the Relation Cache Table and Attribute Cache Table, respectively.
OpenRelTableMetaInfo
The struct OpenRelTableMetaInfo stores whether the given entry in the OpenRelTable, the Relation Cache Table, and Attribute Cache Table are occupied, and also stores the name of the relation if occupied.
typedef struct OpenRelTableMetaInfo {
bool free;
unsigned char relName[ATTR_SIZE];
} OpenRelTableMetaInfo;
The following diagram summarizes the design of this module.